8051 Addressing Modes | Addressing modes of 8051 Microcontroller
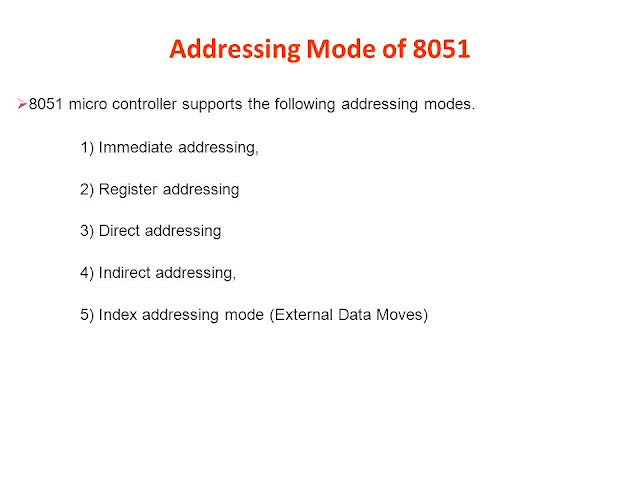
Addressing Modes :- The CPU can access data in a register or in memory or be provided as an immediate value. These various ways of accessing data are called addressing modes. The 8051 provides a total of five distinct addressing modes. They are as follows:- 1) Immediate addressing modes. 2) Register addressing modes. 3) Direct addressing modes. 4) Register indirect - addressing mode. 5) Indexed addressing mode. Let us study different modes with selective examples:- 1) Immediate Addressing mode:- In This addressing mode, the source operated is a co...